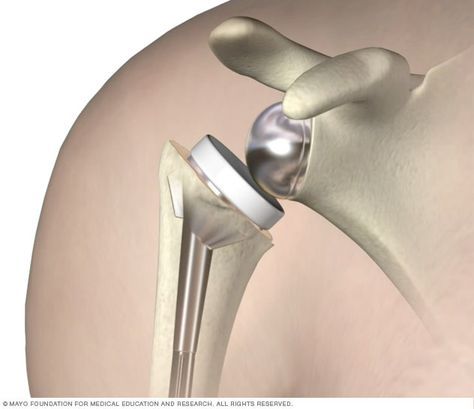
Shoulder Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad
Dr. Praful’s Orthopedic Clinic, Malakpet
with
Advanced Diagnosis & Expert Care by Dr. Kilaru Praful
For shoulder pain or severe joint damage, Shoulder Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad offers a reliable solution. Dr. Praful Kilaru, with over 17 years of experience, uses advanced imaging and precise assessments to plan the best approach. Whether through minimally invasive or traditional surgical techniques, the goal is to restore shoulder function, reduce pain, and help patients regain daily mobility safely and effectively.
What is shoulder replacement surgery?
Shoulder replacement surgery is also known as shoulder arthroplasty. It is a surgical procedure that removes and helps get rid of the damaged bones and tissues in the shoulders. Severe damage in shoulder joints can cause extreme stiffness and excruciating pain to begin with, restricting free movement of the shoulder. Dr.Praful’s orthopedic clinic offers the best shoulder replacement surgery in Hyderabad with the supervision of guidance of highly trained and qualified doctors.
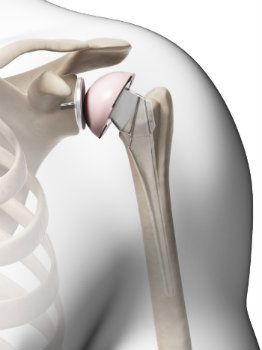
Shoulder Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad – Advanced Treatment for Lasting Pain Relief
Shoulder Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad provides expert care for severe shoulder joint damage caused by arthritis, injury, or wear-and-tear. The procedure aims to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve overall shoulder function. Using advanced imaging and precise surgical planning, Dr. Praful Kilaru tailors treatment to each patient’s condition, age, and activity level, ensuring a safe, effective, and long-term recovery that helps patients return to daily life with confidence.
About the Dr.Praful

- 17+ Years of Excellence in Orthopedics
- MBBS, MS (Orthopaedics)
- AO Trauma Fellowship – Switzerland
- Arthroscopy & Sports Injury Specialist
- Senior Orthopedic Surgeon – Hyderabad
Struggling with Shoulder Pain? Here’s What You Should Know
Shoulder Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad is a specialized treatment for severe shoulder joint damage caused by arthritis, injury, or long-term wear and tear. The goal is to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve overall shoulder function. Using advanced imaging and careful surgical planning, Dr. Praful Kilaru provides personalized care to ensure safe recovery, preserve joint movement, and help patients return confidently to their daily activities.
Common Symptoms Indicating Need for Shoulder Replacement
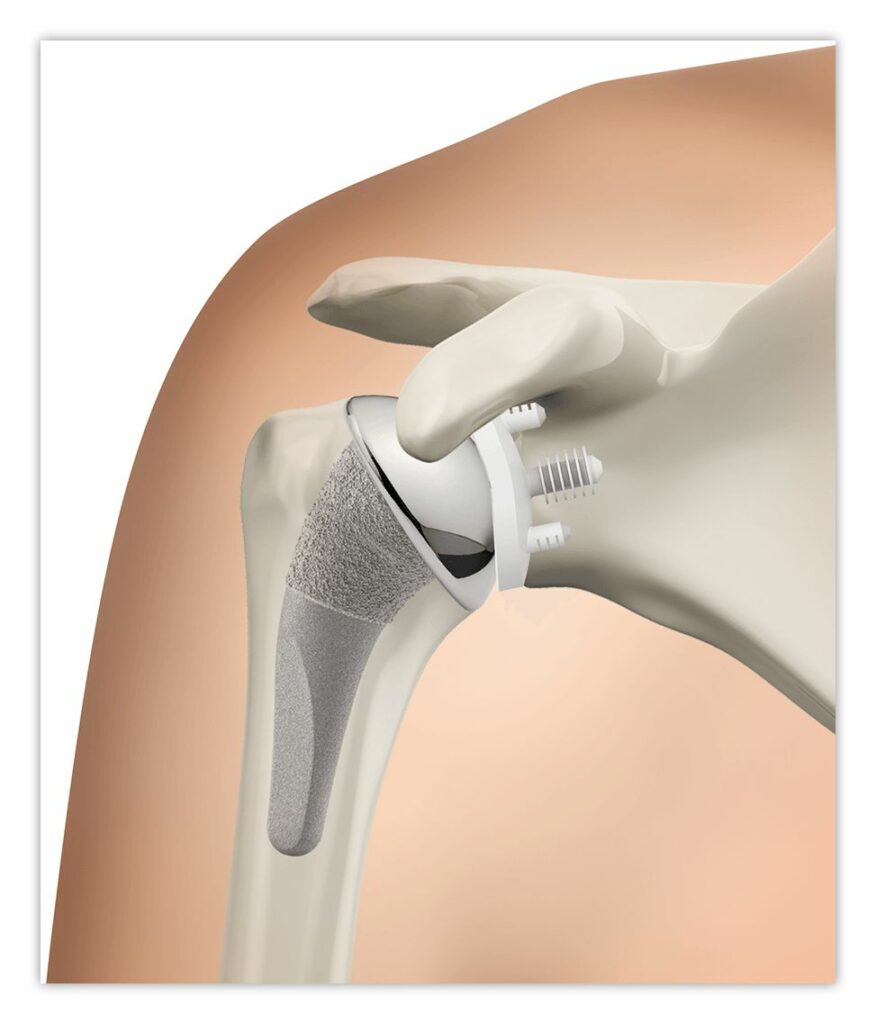
Common Causes in Shoulder Replacement
- Severe arthritis or joint degeneration
- Shoulder injuries from falls or accidents
- Rotator cuff or tendon tears causing joint damage
- Wear-and-tear from repetitive movements
- Bone weakening or fractures affecting shoulder function
Shoulder Replacement Surgery Options in Hyderabad
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications
- Physiotherapy to improve movement and strength
- Activity modification to protect the joint
- Regular imaging to monitor joint health
Surgical Treatments
- Partial or total shoulder replacement
- Minimally invasive shoulder surgery is suitable when suitable
- Reconstruction of damaged joint structures
- Revision surgery for previous failed treatments
Diagnosis for Shoulder Replacement Surgery
Review of shoulder pain
Movement check
X-rays for joint damage
MRI or CT for detail
Why Patients Highly Recommend Dr. Praful
| S.No | Reason | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Strong Educational Background | MBBS, MS Orthopedics, AO Trauma Fellowship (Switzerland) | Qualification |
| 2 | 17+ Years of Clinical Excellence | Successfully treated thousands of patients | Experience |
| 3 | Expert in All Orthopedic Conditions | Knee, spine, shoulder, fractures, sports injuries, pediatric cases | Expertise |
| 4 | Advanced Robotic & Minimally Invasive Surgery | Faster recovery, less pain, precise results | Technology |
| 5 | Honest, Clear & Ethical Treatment | Surgery advised only when truly required | Ethics |
| 6 | High Surgical Success Rate | Thousands of pain-free, satisfied patients | Outcomes |
| 7 | Easy Accessibility – Located in Malakpet | Patients visit from Dilsukhnagar, Amberpet, Chaderghat & more | Location |
| 8 | Excellent Patient Reviews | Known for communication, care & surgical skill | Reputation |
| 9 | Personalized Treatment Plans | Tailored care for every patient | Care Quality |
| 10 | Modern Diagnostic Tools | Accurate assessment with advanced imaging | Diagnostic Quality |
| 11 | Comprehensive Ortho Care | Covers trauma, joint pain, arthritis & sports injuries | Specialty |
| 12 | Friendly & Supportive Team | Smooth experience from consultation to recovery | Patient Support |
| 13 | Fast Recovery Protocols | Focus on minimal downtime and faster healing | Recovery |
| 14 | Transparent Communication | Clear explanation of treatment options | Trust |
| 15 | Affordable Treatment Options | Quality orthopedic care at reasonable pricing | Value |
| 16 | High Patient Satisfaction | Strong word-of-mouth recommendations | Social Proof |
🩺 What Leads to Shoulder Replacement Surgery?
Shoulder replacement is usually recommended when the shoulder joint is severely damaged due to arthritis, injury, or long-term wear. A careful clinical evaluation and imaging help decide whether surgery is the right treatment option.
1. Joint Damage
- Severe shoulder arthritis
- Long-term wear and tear
- Chronic joint pain
2. Injury-Related Causes
- Shoulder fractures
- Rotator cuff tears
- Post-traumatic damage
3. Age & Bone Factors
- Age-related joint degeneration
- Weak or damaged shoulder bones
- Failed previous shoulder surgery
Happy Patients
FAQs – Shoulder Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad
1. How long does the shoulder replacement surgery last?
2. Is shoulder replacement surgery safe?
3. What is the recovery period?
4. How long is the shoulder replacement surgery?
5. What is the cost of the shoulder replacement surgery?
6. What is shoulder replacement surgery?
It is a procedure in which damaged parts of the shoulder joint are replaced with artificial implants to relieve pain and restore function.
7. What is the cost of the shoulder replacement surgery?
Patients with severe arthritis, joint damage, fractures, or long-term shoulder pain that does not improve with non-surgical treatment may need it.
8. Is shoulder replacement surgery safe?
Yes, when performed by an experienced orthopedic surgeon using proper planning and modern techniques, it is a safe and effective procedure.
9. How long does the surgery take?
The surgery usually takes about 1.5 to 2 hours, depending on the condition of the shoulder.
10. How long is the hospital stay?
Most patients stay in the hospital for 2 to 4 days, based on recovery and overall health.
11. Will I be pain-free after surgery?
Most patients experience significant pain relief after recovery, along with improved shoulder movement and function.
12. How long does recovery take?
Initial recovery takes a few weeks, while full recovery with physiotherapy may take 3 to 6 months.
13. Is physiotherapy required after surgery?
Yes, physiotherapy is essential to regain strength, flexibility, and proper shoulder function.
14. How long does a shoulder replacement implant last?
With good care and regular follow-up, shoulder implants often function well for many years, typically around 15–20 years or longer
15. When can I return to daily activities?
Light activities can usually be resumed within a few weeks, while full daily routines return gradually after rehabilitation.