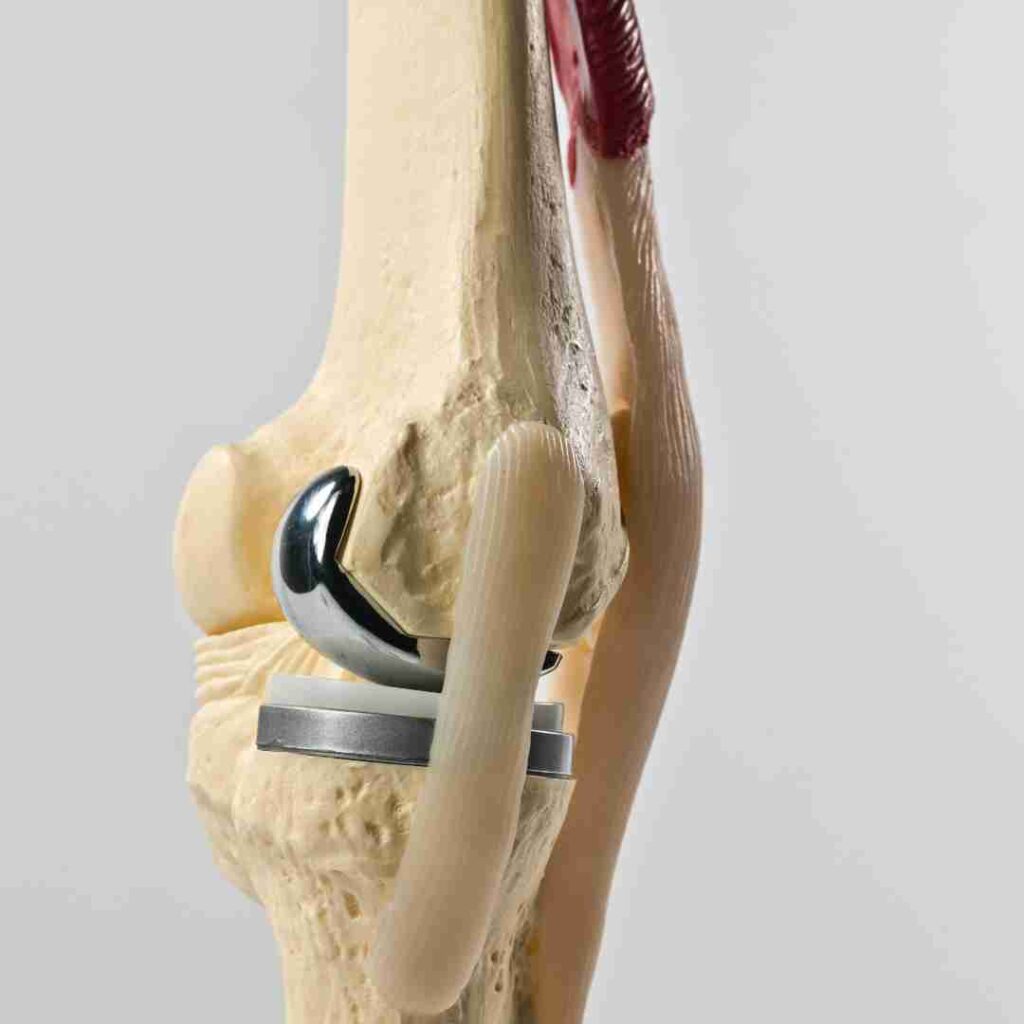
Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad
Dr. Praful’s Orthopedic Clinic, Malakpet
with
Advanced Diagnosis & Expert Care by Dr. Kilaru Praful
Knee problems—like severe arthritis, injury, or degeneration—can significantly affect mobility and quality of life. Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad offers an effective solution for restoring function and relieving pain. With over 17 years of experience, Dr. Praful Kilaru provides trusted care using advanced imaging, precise evaluation, and evidence-based surgical techniques. His approach focuses on improving stability, mobility, and overall knee function, helping patients safely return to their daily activities with confidence and comfort.
What Is Knee Replacement Surgery?
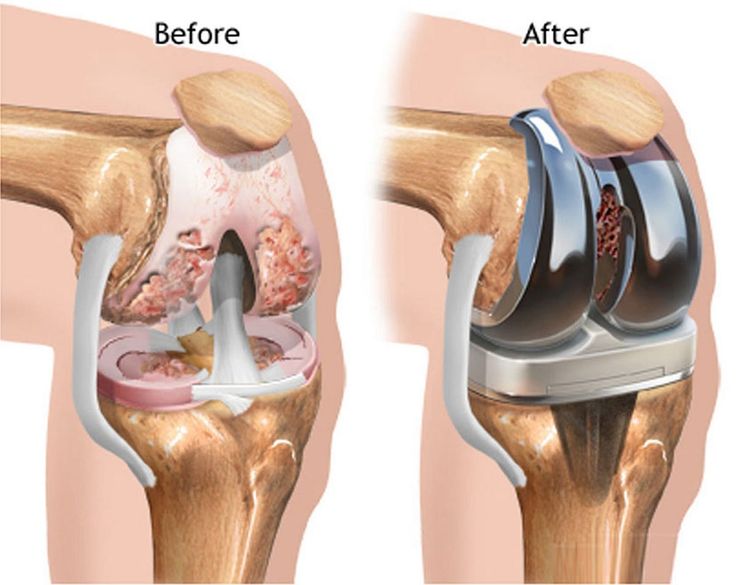
Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad helps people find relief from severe knee pain, stiffness, and mobility issues caused by arthritis or joint damage. The procedure replaces worn-out knee surfaces with modern implants to improve stability and movement. With 17+ years of experience, Dr. Praful Kilaru offers personalized care using advanced imaging and precise planning, helping patients reduce pain, regain strength, and return to everyday life with confidence.
Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad – Expert Care for Restored Mobility
Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad focuses on relieving severe knee pain and restoring function for patients with advanced arthritis, injury, or joint degeneration. The primary goal of the surgery is to replace damaged knee joint surfaces with precise prosthetic implants, improve alignment and stability, enhance mobility, and help patients safely regain their daily activities.
This procedure is often recommended for individuals whose knee pain or stiffness hasn’t improved with medications, physiotherapy, or other conservative treatments. Successful outcomes rely on detailed imaging, careful surgical planning, and specialized orthopedic expertise. Each treatment is personalized, taking into account the patient’s age, activity level, overall health, and the extent of knee damage, ensuring a structured, evidence-based approach that promotes long-term comfort, joint function, and confidence in daily movement.
Top Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad
Dr. Praful Kilaru is a renowned Orthopedic Surgeon and Joint Replacement Specialist in Hyderabad, heading Dr. Praful’s Orthopedic Clinic, located in Malakpet. With over 17 years of experience in orthopedics, trauma care, and sports medicine, Dr. Kilaru is recognized for his precision, advanced surgical methods, and compassionate patient care. At his clinic, Dr. Kilaru combines AI-assisted diagnostic tools and robotic surgery techniques to ensure superior accuracy and faster recovery for patients. He specializes in knee and hip replacements, fracture fixations, ligament reconstructions, and trauma management, offering end-to-end orthopedic care under one roof.Dr. Kilaru is fluent in Telugu, Kannada, English, and Hindi, making communication seamless for patients from diverse backgrounds.

Struggling with Severe Knee Pain? Here’s What You Should Know
Knee Replacement Surgery is a specialized and structured approach designed to relieve severe knee pain and restore joint function for patients with advanced arthritis, injury, or joint degeneration. The main goal of the surgery is to replace damaged knee surfaces with precise prosthetic implants, improve alignment and stability, enhance mobility, and help patients safely return to their daily activities. Timely Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad is crucial to prevent complications such as worsening pain, reduced mobility, stiffness, or long-term joint damage.Dr. Praful Kilaru provides personalized assessments and evidence-based treatment plans, ensuring the best care for every patient.
Common Symptoms That May Indicate You Need Knee Replacement

Common Causes of Knee Problems Requiring Replacement
- Osteoarthritis or joint degeneration
- Injuries or trauma
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Previous knee surgeries
- Age-related weakening of cartilage
Knee Replacement Surgery Options
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Pain relief medications
- Physiotherapy to improve mobility
- Lifestyle changes to reduce knee stress
- Regular imaging to check joint health
Surgical Treatments
- Partial or total knee replacement
- Minimally invasive techniques
- Revision knee surgery if needed
- Customized implants for better function
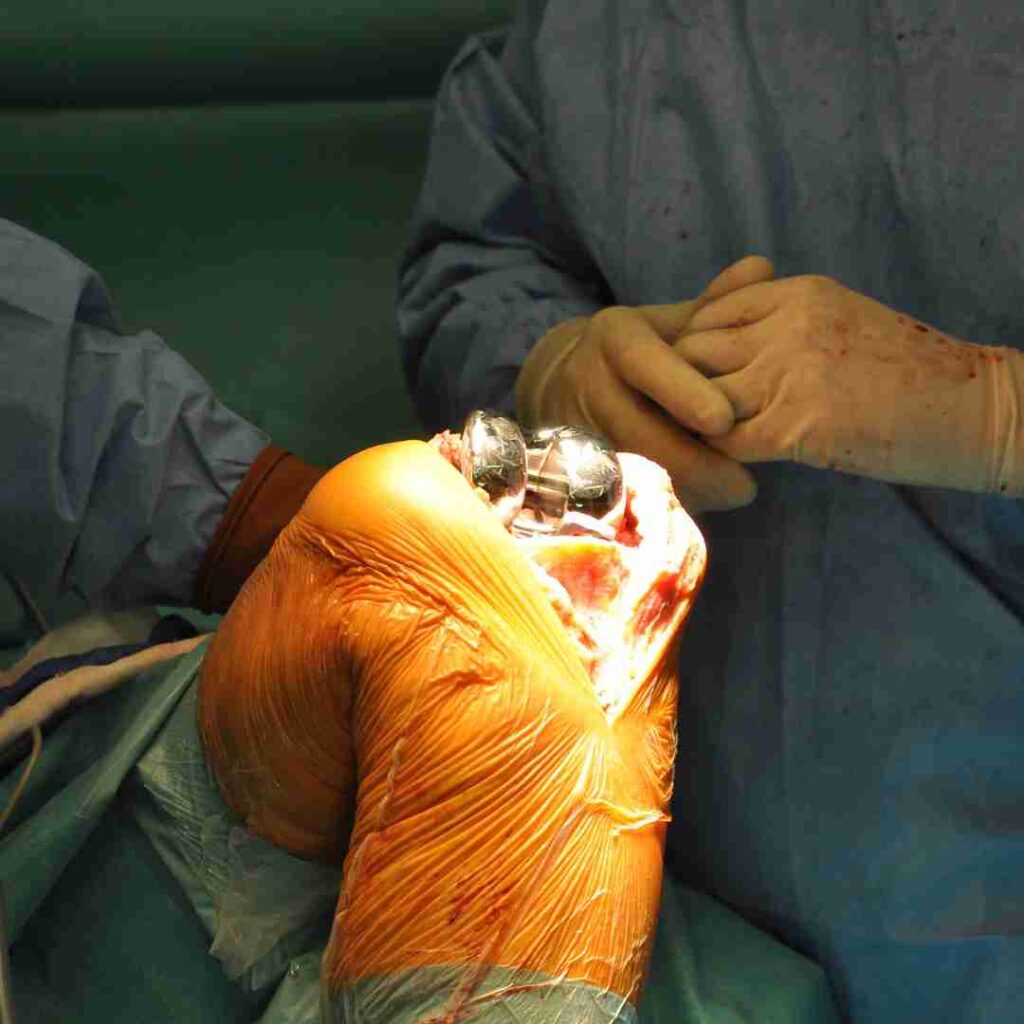
Diagnosis of Complex Fractures
Understand the pain
Check for any swelling
X-rays to view joint damage
CT/MRI for detailed imaging
Why Patients Highly Recommend Dr. Praful
| S.No | Reason | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Strong Educational Background | MBBS, MS Orthopedics, AO Trauma Fellowship (Switzerland) | Qualification |
| 2 | 17+ Years of Clinical Excellence | Successfully treated thousands of patients | Experience |
| 3 | Expert in All Orthopedic Conditions | Knee, spine, shoulder, fractures, sports injuries, pediatric cases | Expertise |
| 4 | Advanced Robotic & Minimally Invasive Surgery | Faster recovery, less pain, precise results | Technology |
| 5 | Honest, Clear & Ethical Treatment | Surgery advised only when truly required | Ethics |
| 6 | High Surgical Success Rate | Thousands of pain-free, satisfied patients | Outcomes |
| 7 | Easy Accessibility – Located in Malakpet | Patients visit from Dilsukhnagar, Amberpet, Chaderghat & more | Location |
| 8 | Excellent Patient Reviews | Known for communication, care & surgical skill | Reputation |
| 9 | Personalized Treatment Plans | Tailored care for every patient | Care Quality |
| 10 | Modern Diagnostic Tools | Accurate assessment with advanced imaging | Diagnostic Quality |
| 11 | Comprehensive Ortho Care | Covers trauma, joint pain, arthritis & sports injuries | Specialty |
| 12 | Friendly & Supportive Team | Smooth experience from consultation to recovery | Patient Support |
| 13 | Fast Recovery Protocols | Focus on minimal downtime and faster healing | Recovery |
| 14 | Transparent Communication | Clear explanation of treatment options | Trust |
| 15 | Affordable Treatment Options | Quality orthopedic care at reasonable pricing | Value |
| 16 | High Patient Satisfaction | Strong word-of-mouth recommendations | Social Proof |
🩺 What Causes the Need for Knee Replacement?
Knee replacement is often needed due to severe joint damage, arthritis, or injury. Proper evaluation helps determine the best treatment approach.
1. Joint Wear & Tear
- Osteoarthritis or cartilage loss
- Rheumatoid or inflammatory arthritis
- Age-related joint degeneration
2. Injury or Trauma
- Previous knee fractures
- Ligament or cartilage injuri
- Sports or accident-related damage
3. Complexity of Knee Damage
- Severe joint deformity
- Multi-part cartilage or bone damage
- Failed previous knee surgeries
Happy Patients
FAQs – Knee Replacement Surgery in Hyderabad
1. How long does the knee replacement surgery last?
2. Is knee replacement surgery an out-patient procedure?
3. What is the recovery time of the surgery?
4. What is the cost of the knee replacement surgery?
5. What are the replacement implants made of?
6. What is knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery involves replacing a damaged knee joint with a prosthetic implant to relieve pain and restore mobility.
7. Who is a candidate for knee replacement?
Patients with severe arthritis, joint degeneration, or chronic knee pain that doesn’t improve with medications or physiotherapy are suitable candidates.
8. How long does the surgery take?
Typically, knee replacement surgery takes 1.5 to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the joint damage.
9. Is knee replacement surgery painful?
Pain is managed with anesthesia during surgery and pain medications afterward. Most patients experience manageable discomfort during recovery.
10. What is the recovery time?
Patients can usually start walking with support within a day or two. Full recovery and return to normal activities typically take 6 to 12 weeks.
11. Are there risks or complications?
Like any surgery, risks include infection, blood clots, or implant-related issues. Choosing an experienced surgeon minimizes these risks.
12. How long does the knee replacement last?
Modern knee implants usually last 15–20 years or more, depending on activity levels and overall health.
13. Will I regain full mobility?
Most patients regain significant mobility and can perform daily activities comfortably. High-impact sports may be limited to protect the implant.
14. Can both knees be replaced at the same time?
Yes, in some cases, bilateral knee replacement is possible, but it depends on your overall health and the surgeon’s assessment.
15. How do I prepare for knee replacement surgery?
Preparation includes medical evaluations, blood tests, imaging, and pre-surgery physiotherapy to strengthen muscles around the knee.