What Is Orthopedic Surgery?

What Is Orthopedic Surgery?
Orthopedic surgery helps you move better, live pain-free, and get back to doing what you love.Orthopedic surgery is a specialized branch of medicine that focuses on diagnosing, treating, repairing, and preventing conditions related to the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and spine. In simple terms, orthopedic surgery helps restore movement, reduce pain, and improve quality of life when the musculoskeletal system is damaged due to injury, disease, or wear and tear.
Many people think orthopedic surgery always means major operations or long hospital stays. In reality, orthopedic care includes both surgical and non-surgical treatments, and surgery is recommended only when other methods are not effective. Orthopedic surgery plays a vital role in helping people return to daily activities, work, sports, and an active lifestyle with better comfort and mobility.
Understanding the Musculoskeletal System
To understand orthopedic surgery, it helps to know what the musculoskeletal system includes. This system provides structure, support, and movement to the body. It consists of:
- Bones
- Joints
- Muscles
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Cartilage
- Spine
Any damage or disorder in these structures can cause pain, stiffness, weakness, or limited movement. Orthopedic surgeons specialize in treating these problems with precision and care.
What Does an Orthopedic Surgeon Do?
An orthopedic surgeon is a doctor trained to manage conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system. Their role goes beyond performing surgery.
Orthopedic surgeons:
- Evaluate pain, injuries, and mobility problems
- Diagnose conditions using X-rays, MRI, CT scans, and physical exams
- Recommend non-surgical treatments such as medication, physiotherapy, or injections
- Perform surgical procedures when necessary
- Guide patients through recovery and rehabilitation
Their ultimate goal is to help patients move better, feel less pain, and regain independence.
When Is Orthopedic Surgery Needed?
Orthopedic surgery is usually considered when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. These treatments may include rest, medications, physiotherapy, braces, or lifestyle changes.
Surgery may be recommended if:
- Pain is severe or long-lasting
- Joint damage affects daily activities
- Fractures are complex or unstable
- Deformities limit movement or posture
- Sports or accident injuries do not heal properly
- Nerve compression causes weakness or numbness
The decision for surgery is always made after careful evaluation and discussion with the patient.
Common Conditions Treated by Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery treats a wide range of conditions. Some of the most common include:
Joint Problems
- Arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis)
- Joint stiffness and degeneration
- Cartilage damage
- Joint instability
Bone Conditions
- Simple and complex fractures
- Delayed or non-healing fractures
- Bone deformities
- Osteoporosis-related fractures
Spine Disorders
- Back pain and neck pain
- Slip disc (herniated disc)
- Spinal stenosis
- Scoliosis and spinal deformities
Sports Injuries
- Ligament tears (ACL, PCL)
- Meniscus injuries
- Tendon ruptures
- Shoulder dislocations
Foot and Ankle Conditions
- Ankle fractures
- Flat foot or high arch problems
- Achilles tendon injuries
- Heel pain and plantar fasciitis
Types of Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery is not a single procedure. It includes many specialized surgical techniques depending on the condition.
Joint Replacement Surgery
This involves replacing damaged joints with artificial implants. Common examples include:
- Knee replacement
- Hip replacement
- Shoulder replacement
These surgeries are often performed for advanced arthritis or joint damage and significantly improve mobility and pain relief.
Fracture Fixation Surgery
When bones break severely or are misaligned, surgery may be needed to fix them using:
- Plates
- Screws
- Rods
- External fixators
This helps bones heal correctly and restores normal function.
Arthroscopic Surgery
This is a minimally invasive procedure where small incisions and a camera are used to repair joint problems. It is commonly done for:
- Knee injuries
- Shoulder injuries
- Ligament and cartilage repairs
Recovery is usually faster compared to open surgery.
Spine Surgery
Spine surgery is done to relieve nerve pressure, correct deformities, or stabilize the spine. Examples include:
- Disc surgery
- Spinal fusion
- Decompression procedures
Not all back pain requires surgery, but when needed, it can greatly improve quality of life.
Sports Injury Surgery
Athletes and active individuals may require surgery for injuries that affect performance and movement. These procedures help restore strength, stability, and confidence.
Non-Surgical vs Surgical Orthopedic Treatment
Not every orthopedic problem needs surgery. In fact, most conditions are first treated non-surgically.
Non-Surgical Treatments Include:
- Pain medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Physiotherapy
- Lifestyle modifications
- Bracing or supports
- Injection therapies
Surgery is considered only when these options fail or when immediate intervention is necessary.
Benefits of Orthopedic Surgery
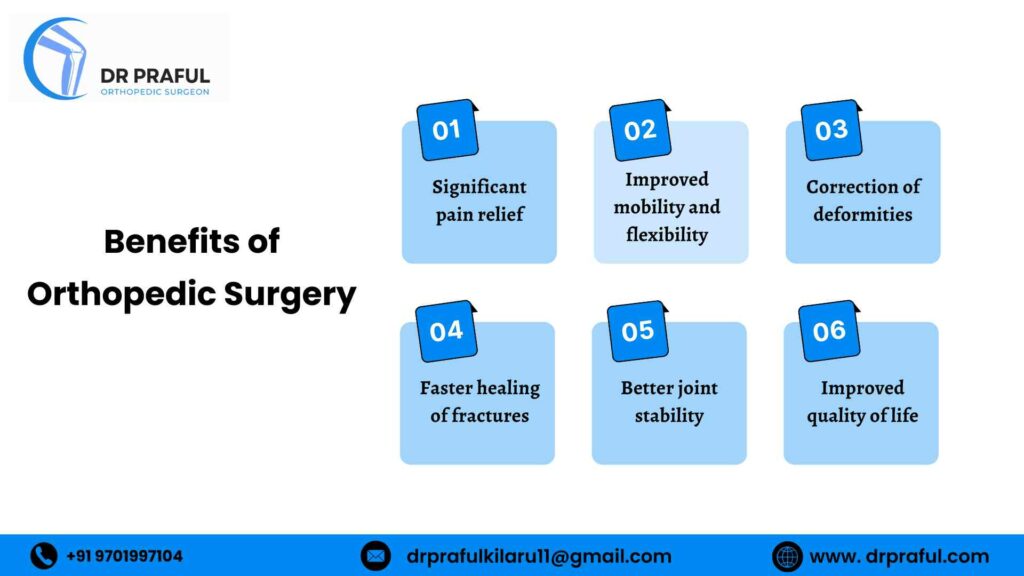
Orthopedic surgery offers several long-term benefits when done at the right time and by an experienced specialist.
Key benefits include:
- Significant pain relief
- Improved mobility and flexibility
- Correction of deformities
- Faster healing of fractures
- Better joint stability
- Improved quality of life
Many patients are able to return to work, sports, and daily activities with renewed confidence.
Recovery After Orthopedic Surgery
Recovery depends on the type of surgery, patient health, and adherence to rehabilitation.
Typical Recovery Process:
- Hospital stay (short or day-care for many procedures)
- Pain management
- Physiotherapy and exercises
- Gradual return to activities
- Follow-up visits
Modern orthopedic techniques focus on faster recovery, minimal pain, and early mobility.
Risks and Safety of Orthopedic Surgery
Like any medical procedure, orthopedic surgery carries some risks. However, with modern technology and experienced surgeons, complications are relatively low.
Possible risks may include:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Stiffness
- Implant issues (rare)
- Delayed healing
Proper pre-surgical evaluation and post-surgical care significantly reduce these risks.
Who Can Benefit from Orthopedic Surgery?
Orthopedic surgery is beneficial for people of all ages, including:
- Elderly patients with joint degeneration
- Young adults with sports injuries
- Accident victims with fractures
- Children with congenital bone conditions
- Working professionals with repetitive stress injuries
Age alone is not a barrier. Overall health and condition severity are more important factors.
Advances in Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery has evolved significantly in recent years. Modern advancements include:
- Minimally invasive techniques
- Computer-assisted surgery
- Improved implant materials
- Faster rehabilitation protocols
- Enhanced imaging technology
These advancements improve accuracy, reduce recovery time, and enhance patient outcomes.
When Should You Consult an Orthopedic Surgeon?
You should consider seeing an orthopedic specialist if you experience:
- Persistent joint or bone pain
- Difficulty walking or moving
- Swelling or deformity
- Recurrent injuries
- Pain that affects daily life or sleep
Early consultation often prevents conditions from worsening and reduces the need for major surgery.
How Orthopedic Surgery Is Planned
Before recommending orthopedic surgery, doctors follow a structured planning process to ensure the best outcome. Surgery is never a rushed decision.
The planning stage usually includes:
- Detailed medical history and physical examination
- Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans
- Evaluation of pain severity and mobility limitations
- Assessment of overall health and lifestyle needs
This careful approach helps the orthopedic surgeon choose the safest and most effective treatment plan for each patient.
Diagnostic Tests Used in Orthopedic Surgery
Accurate diagnosis is the foundation of successful orthopedic surgery. Orthopedic specialists use advanced diagnostic tools to understand the exact cause of pain or dysfunction.
Common diagnostic methods include:
- X-rays to detect fractures and joint degeneration
- MRI scans to assess soft tissue injuries like ligaments and cartilage
- CT scans for complex bone structures
- Blood tests when infection or inflammatory conditions are suspected
These tests help guide precise surgical or non-surgical treatment decisions.
Orthopedic Surgery for Arthritis
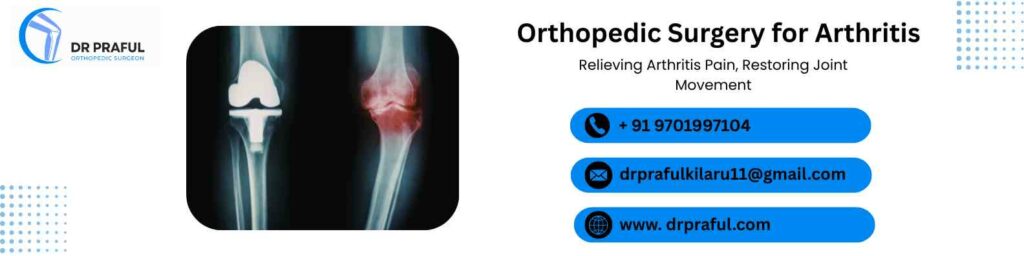
Arthritis is one of the most common reasons people consider orthopedic surgery. When joint damage becomes severe and pain interferes with daily activities, surgical intervention may be recommended.
Orthopedic surgery for arthritis may involve:
- Joint replacement surgery
- Joint resurfacing procedures
- Corrective surgeries to improve alignment
These procedures aim to reduce pain, restore joint function, and improve long-term mobility.
Role of Physiotherapy After Orthopedic Surgery
Physiotherapy is a crucial part of recovery after orthopedic surgery. Surgery repairs the problem, but rehabilitation helps restore strength, flexibility, and coordination.
Post-surgery physiotherapy helps:
- Improve joint movement
- Strengthen surrounding muscles
- Reduce stiffness and swelling
- Prevent future injuries
Following the recommended rehabilitation plan significantly improves surgical outcomes.
Orthopedic Surgery and Pain Management
Pain management is an important concern for patients considering surgery. Modern orthopedic care focuses on minimizing pain before, during, and after surgery.
Pain control may include:
- Medications
- Nerve blocks
- Ice therapy and positioning
- Gradual activity progression
Effective pain management allows patients to recover comfortably and move sooner.
Orthopedic Surgery for Elderly Patients
Age-related bone and joint problems are common, but age alone does not prevent orthopedic surgery. Many elderly patients benefit greatly from surgical treatment.
With proper medical evaluation and post-operative care, elderly patients can experience:
- Improved mobility
- Reduced dependency
- Better balance and confidence
- Enhanced quality of life
Customized treatment plans ensure safety and successful recovery.
Myths and Facts About Orthopedic Surgery
Many misconceptions about orthopedic surgery cause unnecessary fear or delay treatment.
Myth: Orthopedic surgery always means a long recovery
Fact: Many modern procedures allow faster recovery and early movement
Myth: Surgery is only for older people
Fact: Orthopedic surgery benefits people of all ages
Myth: Joint pain should be tolerated
Fact: Early treatment prevents long-term damage
Understanding the facts helps patients make confident decisions.
Cost Considerations in Orthopedic Surgery
The cost of orthopedic surgery varies depending on the type of procedure, hospital facilities, implants used, and rehabilitation needs.
Factors influencing cost include:
- Type of surgery
- Length of hospital stay
- Surgical technology used
- Post-operative care and physiotherapy
Discussing costs in advance helps patients plan treatment without stress.
How to Prepare for Orthopedic Surgery
Proper preparation improves surgical success and recovery.
Preparation may include:
- Medical fitness evaluation
- Stopping certain medications as advised
- Maintaining a healthy diet
- Understanding post-surgery care requirements
Being well-prepared helps reduce anxiety and improve outcomes.
Long-Term Outcomes of Orthopedic Surgery
Most orthopedic surgeries provide long-lasting relief when combined with proper rehabilitation and lifestyle care.
Long-term benefits often include:
- Sustained pain relief
- Improved joint stability
- Better posture and balance
- Increased activity levels
Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and following medical advice help extend surgical benefits.
Conclusion
Orthopedic surgery is a vital medical specialty that helps people regain movement, strength, and independence. While surgery is not always required, it becomes an effective solution when pain, injury, or degeneration limit normal life. With the right diagnosis, timely treatment, and proper rehabilitation, orthopedic surgery can transform lives by restoring comfort and mobility. Understanding your condition and treatment options empowers you to make informed decisions for long-term musculoskeletal health.
Frequently Asked Questions About Orthopedic Surgery
1. What is orthopedic surgery?
Orthopedic surgery is a medical specialty that treats conditions affecting the bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and spine. It aims to reduce pain, restore movement, and improve overall mobility.
2. When is orthopedic surgery recommended?
Orthopedic surgery is recommended when non-surgical treatments such as medication, physiotherapy, or injections do not provide sufficient relief, or when injuries and conditions are severe.
3. Is orthopedic surgery always necessary for joint pain?
No. Most joint pain can be treated without surgery. Orthopedic surgery is considered only when conservative treatments fail or when the condition significantly affects daily activities.
4. What conditions are commonly treated with orthopedic surgery?
Orthopedic surgery commonly treats arthritis, fractures, sports injuries, ligament tears, spine disorders, joint degeneration, and congenital bone deformities.
5. Is orthopedic surgery safe?
Yes, orthopedic surgery is generally safe when performed by experienced surgeons using modern techniques. Pre-surgical evaluation and proper post-operative care reduce risks significantly.
6. How long does recovery take after orthopedic surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery, patient age, and overall health. Minor procedures may recover in weeks, while major surgeries may take several months with rehabilitation.
7. Does orthopedic surgery require a long hospital stay?
Not always. Many orthopedic procedures are minimally invasive and may require only a short hospital stay or even day-care admission.
8. What is the role of physiotherapy after orthopedic surgery?
Physiotherapy helps restore strength, flexibility, and joint movement after surgery. It is essential for faster recovery and long-term success of orthopedic treatment.
9. Can elderly patients undergo orthopedic surgery?
Yes. Age alone is not a limitation. Many elderly patients benefit from orthopedic surgery when they are medically fit and properly evaluated before the procedure.
10. Is orthopedic surgery painful?
Pain is managed effectively using medications, modern anesthesia techniques, and rehabilitation protocols. Most patients experience manageable discomfort that improves steadily with recovery.
11. What are minimally invasive orthopedic surgeries?
Minimally invasive orthopedic surgeries use smaller incisions and advanced instruments to treat joint and bone problems. These procedures usually result in less pain and faster recovery.
12. What is the difference between an orthopedic doctor and an orthopedic surgeon?
An orthopedic doctor diagnoses and manages bone and joint conditions, while an orthopedic surgeon is trained to perform surgical procedures when surgery is required.
13. Can orthopedic surgery improve quality of life?
Yes. Orthopedic surgery often significantly improves mobility, reduces chronic pain, and helps patients return to daily activities, work, and sports.
14. How should I prepare for orthopedic surgery?
Preparation may include medical tests, lifestyle adjustments, medication review, and understanding post-surgery care instructions. Proper preparation improves surgical outcomes.
15. When should I consult an orthopedic surgeon?
You should consult an orthopedic surgeon if you have persistent joint or bone pain, difficulty moving, repeated injuries, or pain that affects daily life and sleep.
